Mike Lee
Updated: Mar 27, 2024
How to create a more effective RFI process
Efficient management of RFIs is critical to project success. However, this process is often overlooked. This guide will explain the ins and outs of RFIs and offer tips on how you can streamline this process.
Research shows that the average construction project will have over 800 RFIs!
This figure surges past 1,400 for endeavors extending beyond five years. Response times vary from 6.4 to 9.7 days depending on the region. Particularly noteworthy is the disproportionate impact of RFIs on smaller projects, where those valued between $5 million and $50 million encounter a staggering 17.2 RFIs per $1 million of construction cost.
At their essence, RFIs serve as vital conduits for information exchange. They help project stakeholders eliminate ambiguities and ensure all parties are aligned on specifics. Yet, without careful oversight, the burden of managing this process can lead to inefficiencies and reduce project profit.
First, what is an RFI in Construction Administration?
An RFI (or Request for Information) is a workflow process that seeks to clarify plans, drawings, specifications, or agreements. This ensures all stakeholders have a comprehensive understanding of specific project aspects or requirements.
In construction, an RFI becomes necessary when there's missing information in the construction documents. RFIs are typically initiated by the general contractor, but may also be initiated by subcontractors. Upon receiving responses from the client or architect, RFI responses are shared with all relevant parties.
Historically, RFIs were managed through spreadsheets. However, today many organizations use construction management software tools or document management systems to streamline the RFI process. Software tools such as Layer facilitate instantaneous sharing of information. In turn, this saves time reducing expenses and lowering the risk of late project delivery.
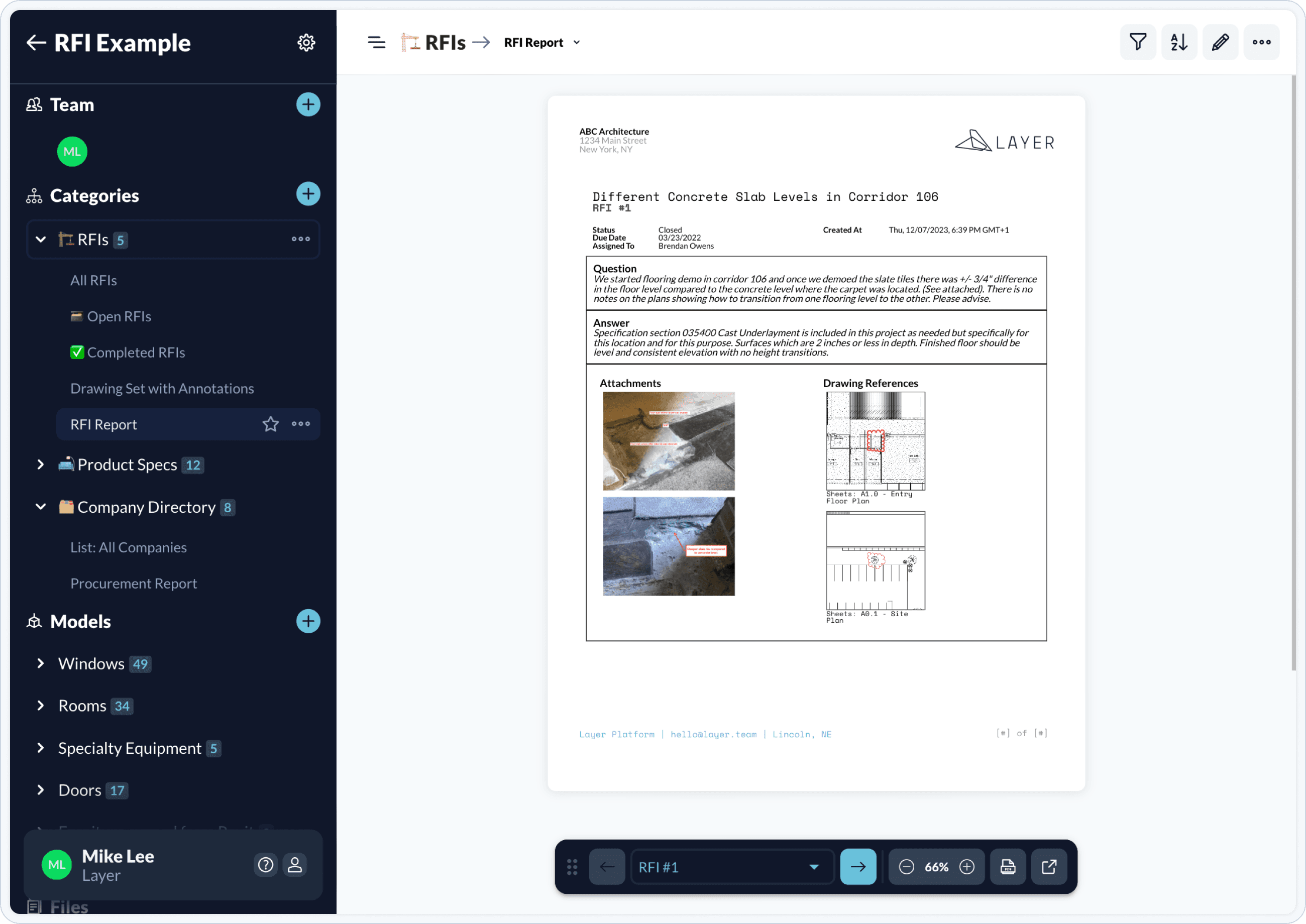
What is Typically Included in an RFI?
RFI format may vary based on the specific information being requested. However, there are several common components typically included in an RFI within the construction industry, such as:
A question, objective, or summary of the request
A proposed timeline for resolution
Documentation such as photos, spec sheets, or highlights from relevant documents
Details on who is submitting the RFI and appropriate due dates
What is the difference between RFIs & RFPs
RFIs are often confused with RFPs by those unfamiliar with Design & Construction. Within a procurement context, an RFI is is often used to assess the capabilities and offerings of potential suppliers. They allows the purchasing team to gather detailed information about the products, services, and qualifications of various vendors. Within this context, RFPs are an invitation to submit a bid for those products or services. Another common acronym, RFQs (Request for Quotes), request pricing for specific products or services.
The RFI Process in Construction
Creation of RFIs in the construction process involves several key steps:
Drafting the RFI
Submission to the appropriate party
Awaiting a response
Incorporating that response into the project workflow
This process ensures that any issues or uncertainties are addressed promptly, minimizing delays and cost overruns.
Types of RFIs
RFIs can range from queries about material specifications to requests for clarification on design drawings or construction techniques. Some common types include:
Design Clarification RFIs
Design Clarification RFIs seek further details or explanations about the design aspects of a project. They are often raised by contractors or subcontractors who require a deeper understanding of the drawings or specifications provided by the project’s architects or engineers. Design clarification RFIs ensure that the construction adheres to the intended design, preventing costly modifications later in the project.
Construction Coordination RFIs

Coordination RFIs are essential in complex projects involving multiple trades or disciplines. They address the logistical and scheduling aspects of work execution. This ensures that the effort of all parties is synchronized. This type of RFI may cover topics like work sequencing, site access for different contractors, or timing of material deliveries.
Material or Product Substitution RFIs
When specified materials are unavailable, too expensive, or deemed unsuitable for some reason, contractors may suggest alternatives through a material or product substitution RFI. These RFIs must include detailed comparisons to justify the substitution. This ensures that the alternative materials meet the project’s standards and requirements.
Site Condition Inquiries
Site condition RFIs arise when the actual site conditions differ from those described in the construction documents. These can cover unforeseen obstacles, discrepancies in existing structures, or environmental concerns that could impact the project. Addressing these issues early through RFIs helps in mitigating risks associated with delays and cost overruns.
Constructability Issues
Constructability RFIs question the feasibility of executing the design as specified in the construction documents. Contractors raise these RFIs when they believe a design detail cannot be constructed in the proposed manner. They may also suggest a more efficient alternative that could save time or reduce costs without compromising quality.
Timing and Phasing
These RFIs seek to adjust the project schedule or phase certain tasks differently from the initial plan. They are crucial for dynamic project environments where external factors, such as weather conditions or delayed permits, affect the original project schedule.
When a contractor identifies a potential improvement to the project’s design that could enhance functionality, reduce costs, or mitigate potential issues, they may submit a design change RFI. This type of RFI requires a detailed explanation of the proposed change and its benefits to the project.
Utility Conflict RFIs

Utility conflict RFIs are raised when existing utilities (e.g., water, gas, electricity) conflict with the planned construction activities. These RFIs are critical for preventing damage to existing infrastructure and ensuring the safety of the construction environment.
Tips on Streamlining the Construction RFI Process
Craft a Clear and Concise Request
Writing an RFI involves articulating the query clearly and concisely, providing sufficient background information, and, if possible, suggesting potential solutions or alternatives. A well-crafted RFI should be easy to understand, easy to reply to, and aid smooth progression of the project.
Respond to RFIs in a Timely Manner
Responding to an RFI requires the recipient to provide the requested information or clarification in a clear and comprehensive manner. Timely responses are crucial to maintain project momentum and avoid unnecessary delays. The RFI response should address the query directly, offering solutions or further instructions as needed.
Add Relevant Supporting Documentation
Add photos, files, and any other information that the other party may need to make a decision.
Use RFI-Specific Tools Instead of Spreadsheets
Spreadsheets and Word documents are static. Even if the document is hosted on a file-sharing service, they may not instantly update and they do not have built-in notification capabilities.
Pro tip: Software tools such as Layer can facilitate a more efficient RFI process by instantly alerting relevant parties and adding context to the RFI by linking directly to models, floorplans, photos, and documents. View Layer RFI Template →
Standardize Your RFI Process and Deploy RFI Templates
RFI templates are standardized forms used to ensure that all necessary information is provided when an RFI is submitted. A templatized approach maintains consistency and completeness across all RFIs issued. This makes it easier for recipients to understand and respond to the request.
Conclusion
Responding to RFIs can be seem like a burden, but they're an essential part of the Construction Administration Process. Making this process as straightforward as possible will help you and the General Contractor stay on the same page so your design vision meets reality and they can deliver the building on time to the Owner so they stay happy.
Remember: Happier Clients = More Projects




